Your application's pressure, sealing, and installation limits determine whether to use a raised-face vs. flat-face flange. Medium- to high-pressure systems benefit from a raised-face flange’s protruding sealing surface, which focuses gasket pressure. Smooth, level, flat-face flanges transmit stress equally across fragile materials like cast iron or glass-lined equipment. Understanding these basic distinctions helps engineers choose the best flange design for leak-free industrial pipe connections.
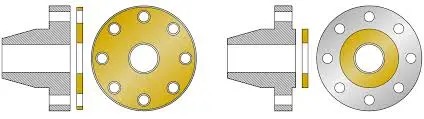
Understanding Flange Sealing Surface Fundamentals
Flange design is crucial to piping system integrity. Gaskets generate pressure-tight pipe connections depending on their sealing surface.
Industrial applications use two main flange faces:
- Raised Face (RF)—Features a raised gasket seating surface within the bolt circle.
- Flat Face (FF)—Provides a flat sealing surface across the entire flange face.
- Ring Type Joint (RTJ) flanges for extreme conditions use metal ring gaskets.
Each flange finish meets operating needs. Gasket selection, installation, and performance depend on the option.
In pressure ratings above ASME Class 150, ASME B16.5 standards recognize raised face flanges as providing improved sealing performance compared to flat face designs due to concentrated gasket compression. For reliable medium-pressure sealing (ASME Class 150 to Class 600), higher face flanges are better.
Raised Face Flange Characteristics and Applications
Raised face flanges extend 1.6 mm (1/16 inch) beyond the bolt circle. Elevating the gasket improves seal integrity at different pressures. When comparing raised-face vs. flat-face flanges, it's essential to consider the specific requirements of your application, as each type has distinct characteristics that influence performance.
Key technical specifications include:
- Standard raised face height: 1.6 mm (1/16") for ASME Class 150–300 and 6.4 mm (1/4") for Class 400 and above, per ASME B16.5
- Pressure ratings: 150# through 2500# classes
- Surface finish: 125–250 μin Ra (roughness average)
- Gasket types: Spiral wound, composite, rubber-based materials
Manufacturing precision affects sealing performance significantly. CNC-machined surfaces ensure consistent finish quality and dimensional accuracy across production batches.
Industrial testing demonstrates raised face flanges maintain seal integrity through 1000+ thermal cycles without gasket replacement. This durability reduces maintenance expenses and minimizes unplanned downtime.
Common applications encompass petrochemical processing, power generation, and water treatment facilities where reliable sealing justifies the additional material costs.
If you need flanges for chemical processing or high-temperature steam lines, then raised face designs provide superior long-term reliability.
Flat Face Flange Design and Performance Benefits
Flat-face flange construction eliminates raised surfaces, creating uniform stress distribution across the entire flange face. This design prevents stress concentration that could damage brittle flange materials.
Essential design parameters include:
- Uniform surface contact across bolt circle diameter
- Maximum pressure rating: typically 150 class applications
- Compatible materials: cast iron, glass-lined steel, certain plastics
- Full-face gasket coverage for optimal stress distribution
Flat face configurations excel in low-pressure systems where flange material integrity outweighs maximum sealing efficiency. Cast iron flanges particularly benefit from this stress-distributing design.
Laboratory testing reveals flat face flanges reduce stress concentration by 40% compared to raised face alternatives when used with brittle materials. This reduction significantly extends flange service life.
Installation procedures are simplified with flat-face designs since gasket positioning requires less precision. Full-face gaskets accommodate slight alignment variations during assembly.
If you need flanges for cast iron piping systems or glass-lined equipment, then flat face designs prevent material cracking and extend service life.
Technical Performance Comparison Analysis
Direct comparison between flange types reveals distinct performance characteristics across multiple operational parameters.
| Performance Factor | Raised Face | Flat Face |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Rating | 150# - 2500# | 150# maximum |
| Sealing Efficiency | 95-98% | 85-90% |
| Material Compatibility | Steel, stainless steel | Cast iron, glass-lined |
| Gasket Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Installation Complexity | Moderate | Simple |
Pressure testing data from industry gasket and flange leakage evaluation practices demonstrate that raised-face flanges can achieve lower leak rates under equivalent bolt loads and gasket conditions. Flat face assemblies generally exhibit higher leakage under identical test setups, depending on gasket type and surface finish.
Temperature cycling performance varies significantly between designs. Raised face flanges tolerate thermal expansion differences more effectively due to concentrated gasket loading.
Cost analysis reveals initial material expenses favor flat-face designs, while lifecycle costs often favor raised-face applications due to reduced maintenance requirements.
If you need maximum sealing performance for critical applications, then raised-face vs. flat-face flanges justify the additional investment through reduced operational risks.
Material Selection and Manufacturing Standards
Flange material selection directly impacts sealing surface performance and operational longevity. Manufacturing standards ensure consistent quality across suppliers.
Primary material categories include:
- Carbon Steel - ASTM A105 for standard pressure applications
- Stainless Steel—ASTM A182 F304/F316 for corrosive environments
- Alloy Steel—ASTM A182 F11/F22 for high-temperature service
- Cast Iron—ASTM A126 Class B for low-pressure systems
Manufacturing quality affects sealing performance dramatically. CNC machining produces dimensional tolerances within ±0.025 mm, ensuring gasket contact uniformity.
Hot-dip galvanizing provides corrosion protection, extending service life by 15–25 years in many industrial and coastal environments, depending on exposure severity. This coating process meets ASTM A123 specifications for industrial applications.
Material traceability documentation supports quality assurance programs. Mill test certificates (MTC) verify chemical composition and mechanical properties for each production heat.
RAYOUNG maintains comprehensive quality control throughout manufacturing processes, ensuring every flange meets specified dimensional and surface finish requirements.
If you need certified flanges for export applications or government projects, then GOST-R and SGS certifications provide essential compliance documentation.
Installation Guidelines and Best Practices
Proper installation techniques maximize flange performance and prevent premature failure. Following established procedures ensures reliable operation throughout the design service life.
Critical installation steps include:
- Surface inspection for damage, contamination, or dimensional deviations
- Gasket selection based on fluid compatibility and pressure requirements
- Bolt torque application using approved sequences and values
- Final inspection for alignment and gap measurements
Gasket installation varies between flange types. Raised face designs require precise gasket centering within the raised area. Flat-face assemblies use full-face gaskets extending to the bolt circle.
Bolt torque specifications follow ASME PCC-1 guidelines. Proper torque ensures uniform gasket compression without overstressing flange materials or bolting.
Field testing demonstrates that correctly installed flanges achieve design pressure ratings with safety margins consistent with applicable design codes. Improper installation reduces this margin significantly.
Documentation requirements include torque records, gasket specifications, and dimensional verification data. These records support maintenance planning and troubleshooting activities.
If you need reliable installation support for critical projects, then partnering with experienced suppliers ensures proper assembly procedures and documentation.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Economic factors influence flange selection beyond initial purchase price. Lifecycle cost analysis provides comprehensive comparison data for informed decision-making.
Cost components include:
- Initial material and manufacturing expenses
- Installation labor and equipment requirements
- Maintenance intervals and replacement parts
- Downtime costs associated with leakage or failure
Raised-face vs. flat-face flanges typically cost 10–15% more than flat-face alternatives initially. However, reduced maintenance requirements often justify this premium over 20-year service periods.
Gasket costs vary significantly between applications. Raised-face vs. flat-face flange designs typically use smaller, specialized gaskets costing 20-30% more than full-face alternatives. However, longer service intervals offset this difference.
Unplanned maintenance costs represent the largest economic risk. System downtime for leak repairs can exceed $10,000 per hour in process industries, making reliable sealing essential.
Bulk purchasing arrangements reduce unit costs while ensuring inventory availability for planned maintenance activities. Long-term supplier partnerships provide pricing stability and technical support.
If you need cost-effective solutions for large infrastructure projects, then establishing supplier partnerships with certified manufacturers optimizes both quality and pricing.
RAYOUNG's Flange Manufacturing Advantages
RAYOUNG delivers superior flange solutions combining advanced manufacturing capabilities with comprehensive quality assurance programs. Our expertise spans diverse industrial applications requiring reliable sealing performance.
Manufacturing Excellence
- Precision CNC Machining—Advanced equipment ensures surface finishes within ±0.025 mm tolerance for optimal gasket contact
- Material Traceability—Complete MTC documentation tracks every flange from raw material through final inspection
- Quality Certifications—ISO 9001:2015, GOST-R, and SGS certifications validate manufacturing processes and export compliance
- Standard Compliance—Full adherence to ANSI, DIN, and JIS flange specifications with RF, FF, and RTJ facing options
- Corrosion Protection—Hot-dip galvanizing services extend service life in challenging environments.
Product Range Capabilities
- Pressure Ratings—Complete range from 150# through 2500# class specifications
- Material Options—Carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel grades for diverse applications
- Size Availability—Standard dimensions from 1/2" through 48" diameter, with custom sizes available
- Surface Finishes—Raised face, flat face, and RTJ configurations for specific sealing requirements
- Testing Capabilities—Hydrostatic testing and dimensional verification ensure performance specifications
Customer Support Services
- Technical Consultation—Engineering support for flange selection and application optimization
- Delivery Reliability—Established supply chains ensure on-time delivery for project schedules
- Global Reach—Export capabilities serving domestic and international markets
- Inventory Management—Stocking programs support distributor networks and end-user requirements
- Documentation Support—Complete certification packages for government and infrastructure projects
Innovation and Development
- Continuous Improvement—Investment in manufacturing technology enhances product quality and delivery performance.
- Application Expertise—Deep understanding of industry requirements from water treatment to petrochemical processing
- Custom Solutions—Engineering capabilities for special applications and non-standard requirements
- Cost Optimization—Value engineering services help customers achieve project objectives within budget constraints.
- Long-term Partnerships—A collaborative approach builds lasting relationships with EPC contractors, distributors, and end users.
Conclusion
Selecting between raised-face and flat-face flanges requires careful consideration of pressure requirements, material compatibility, and operational conditions. Raised face designs excel in medium- to high-pressure applications where sealing integrity justifies additional costs. Flat-face configurations serve low-pressure systems with brittle materials requiring stress distribution. Understanding these fundamental differences enables informed decisions that optimize system performance, minimize lifecycle costs, and ensure reliable operation. RAYOUNG's comprehensive manufacturing capabilities and quality certifications support successful project execution across diverse industrial applications.
Choose RAYOUNG for Reliable Raised Face vs Flat Face Flange Solutions
RAYOUNG's comprehensive flange manufacturing capabilities address every aspect of your sealing requirements. Our CNC-machined surfaces, complete MTC traceability, and hot-dip galvanizing options ensure reliable performance across ANSI, DIN, and JIS standards. Whether you're an EPC contractor managing complex projects or a distributor serving local markets, our ISO 9001:2015 certified facilities deliver consistent quality with GOST-R and SGS export compliance. Contact our technical team to discuss your specific raised-face vs. flat-face flanges supplier requirements and discover how our solutions minimize project risk while meeting critical deadlines. Reach out to us at info@hb-steel.com for immediate assistance.
References
1. American Society of Mechanical Engineers. "ASME B16.5 - Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings: NPS 1/2 Through NPS 24 Metric/Inch Standard." New York: ASME Press, 2020.
2. Deutsches Institut für Normung. "DIN EN 1092-1 - Flanges and Their Joints - Circular Flanges for Pipes, Valves, Fittings and Accessories, PN Designated - Part 1: Steel Flanges." Berlin: DIN Standards, 2019.
3. Japanese Standards Association. "JIS B 2220 - Steel Pipe Flanges." Tokyo: JSA Group, 2018.
4. American Society for Testing and Materials. "ASTM F1387 - Standard Specification for Performance of Piping and Tubing Closure Seals." West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2021.
5. Process Industry Practices. "PIP PNRF0301 - Pipe Flange Design Guide." Austin: Process Industry Practices, 2017.
6. British Standards Institution. "BS EN 12560-1 - Flanges and Their Joints - Gaskets for Class-Designated Flanges." London: BSI Standards, 2019.






