Flange Bolt Patterns Explained: ASME vs DIN vs JIS Standard Dimensions
While working with pipeline systems that meet different international standards, engineers and procurement experts need to know how to read flange bolt patterns. As important connection points in piping systems, industrial flanges are what decide compatibility, safety, and performance. Looking at the main differences between ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers), DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung), and JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards) flange standards, this guide helps professionals make smart choices for their business needs. Depending on the standard, there are different size requirements, bolt hole arrangements, and pressure limits that have an immediate effect on the reliability and efficiency of the system.
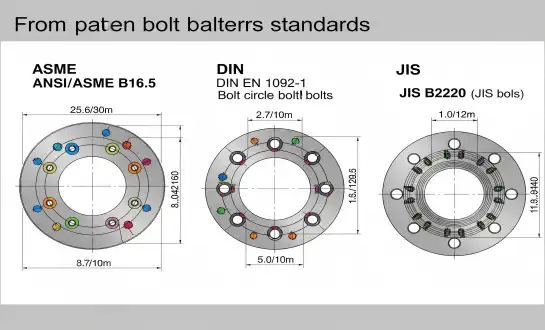
ASME Flange Bolt Pattern Standards and Specifications
Dimensional Requirements for ASME B16.5 Standards
ASME B16.5 standards establish precise dimensional requirements for industrial flanges used in North American markets and international projects following American specifications. The standard defines bolt circle diameters, bolt hole quantities, and spacing requirements that ensure consistent performance across pressure classes ranging from 150 to 2500. Industrial flanges manufactured under ASME standards feature specific bolt hole diameters, typically ranging from 5/8 inch to 1-1/4 inches depending on flange size and pressure rating. The bolt circle diameter increases proportionally with nominal pipe size, creating standardized patterns that facilitate interchangeability between different manufacturers. These dimensional specifications ensure that industrial flanges maintain structural integrity under various operating conditions while providing reliable sealing capabilities essential for critical applications.
Pressure Class Variations and Bolt Configurations
ASME standards categorize industrial flanges into distinct pressure classes, each requiring specific bolt configurations to handle designated operating pressures and temperatures. Class 150 flanges utilize fewer bolts with larger spacing compared to higher pressure ratings, while Class 2500 flanges incorporate numerous closely-spaced bolts to distribute stress effectively. The bolt pattern density increases significantly with pressure class, ensuring adequate clamping force distribution across the flange face. Industrial flanges in Class 600 and above often require special alloy bolting materials to withstand extreme conditions, while maintaining the standardized hole patterns that define ASME compatibility. This organized way of classifying pressure lets engineers choose the right industrial flanges for each system while making sure that the bolt patterns always work together.
Material Specifications and Quality Standards
ASME standards specify material requirements for industrial flanges, including chemical composition, mechanical properties, and manufacturing processes that affect bolt pattern integrity. Carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel flanges must meet specific ASTM material specifications while maintaining precise bolt hole dimensions and surface finishes. The manufacturing tolerances for bolt holes are strictly controlled to ensure proper gasket seating and uniform bolt loading across all connection points. Industrial flanges manufactured to ASME standards undergo rigorous testing procedures, including dimensional verification, material testing, and pressure testing to validate compliance with established specifications. During the manufacturing process, quality control measures make sure that bolt patterns stay accurate. This keeps fitting problems from happening and guarantees long-term dependability in tough industrial settings.
DIN European Flange Standards and Dimensional Analysis
DIN EN 1092-1 Standard Requirements
DIN EN 1092-1 represents the European standard for industrial flanges, establishing dimensional requirements that differ significantly from ASME specifications in bolt pattern configurations and pressure rating systems. European industrial flanges utilize metric dimensions throughout their design, with bolt circle diameters, bolt hole sizes, and spacing calculated in millimeters rather than imperial units. The standard defines pressure nominal (PN) ratings from PN6 to PN400, each corresponding to specific bolt patterns that ensure adequate strength and sealing performance. DIN industrial flanges feature unique bolt hole quantities and arrangements that optimize stress distribution while accommodating European manufacturing practices and material availability. The standard stresses precise production with close tolerances on dimensions to make sure that products made by different European companies and used in different ways always work the same way.
Metric Dimensioning and European Manufacturing
DIN standards embrace metric dimensioning systems that influence every aspect of industrial flanges design, from bolt hole diameters to face-to-face dimensions and overall flange thickness. European manufacturers produce industrial flanges with bolt patterns optimized for metric hardware, utilizing standard metric bolt sizes that simplify procurement and maintenance procedures. The bolt spacing calculations follow mathematical progressions that distribute stress evenly while accommodating standard metric bolt sizes readily available in European markets. DIN industrial flanges often feature raised face configurations with specific surface finish requirements that enhance sealing performance when combined with European gasket standards. Manufacturing processes for DIN flanges emphasize precision machining capabilities that maintain tight tolerances essential for proper bolt pattern alignment and gasket compression.
Compatibility Considerations with International Systems
DIN industrial flanges present unique challenges when interfacing with ASME or JIS systems due to fundamental differences in bolt patterns, pressure ratings, and dimensional specifications. Conversion between DIN and ASME systems often requires adapter flanges or complete system redesign to accommodate different bolt patterns and pressure class designations. When engineers define industrial flanges for international projects that may include parts from different standards organizations, they need to carefully look at the requirements for compatibility. The number, spacing, and shapes of bolt holes can vary a lot between DIN and other standards, which can have a big effect on project costs and installation times. When putting together industrial flanges from different international standards, it's important to know these limits in order to complete the project successfully and make sure the system works well in the long term.
JIS Japanese Industrial Standards for Flange Systems
JIS B2220 Standard Specifications
JIS B2220 establishes comprehensive specifications for Japanese industrial flanges, incorporating unique design elements that reflect Japanese manufacturing capabilities and application requirements. The standard establishes bolt designs that make the best use of material while also providing the right level of strength for tough industrial uses. Japanese industrial flanges have unique bolt hole arrangements that are different from both ASME and DIN standards. To properly specify and install them, you need to know a lot about these differences. JIS standards stress small designs that use as little material as possible while keeping the structure strong by using the best bolt patterns and face configurations. The method for rating pressure uses kilogram-force per square centimeter (kgf/cm²) units, which makes pressure class names that need to be carefully converted when using other international standards.
Manufacturing Excellence and Quality Control
Japanese manufacturers of industrial flanges maintain exceptional quality control standards that ensure consistent bolt pattern accuracy and surface finish quality across production runs. JIS standards specify precise manufacturing tolerances for bolt holes, face finishes, and dimensional accuracy that exceed many international requirements. Industrial flanges with better dimensional consistency and long-term dependability are the result of a focus on continuous improvement and quality management systems. Japanese production methods use advanced machining technologies to get accurate placement of bolt holes and high-quality surface finishes that are necessary for the gasket to work at its best. For JIS industrial flanges, quality control measures include checking all dimensions, making sure the material is correct, and testing the flanges under pressure to make sure they meet set standards.
Applications in Asian Markets and Export Considerations
JIS industrial flanges serve diverse applications throughout Asian markets, where Japanese manufacturing quality and reliability have established strong market positions. Because JIS flanges have specific bolt patterns and size requirements, they need to be designed by people who know a lot about them for Asian markets or export purposes. Industrial flanges made to JIS standards are often a cost-effective way to complete projects that need high-quality parts that have been shown to work well in the past. When exporting JIS flanges, you need to make sure that they meet the standards of the country where they are going by checking the dimensions and making sure that all the necessary paperwork is in order. Companies that do business in Asia or buy industrial flanges from Japanese makers for projects in other countries need to understand JIS specifications.
Conclusion
The main changes between ASME, DIN, and JIS flange bolt patterns have a big effect on how industrial piping systems are designed, bought, and put together. Each standard has its own benefits that are based on regional needs and manufacturing skills. Engineers can make decisions that improve system speed while also making sure that it is compatible and will last for a long time when they understand these differences. To properly specify industrial flanges, you need to carefully think about the bolt patterns, pressure ratings, and size requirements that are unique to each standard.
HEBEI RAYOUNG PIPELINE: Premier Industrial Flanges Manufacturers
At HEBEI RAYOUNG PIPELINE TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD., we excel in manufacturing superior industrial flanges that meet ASME, DIN, and JIS standards with exceptional precision and reliability. With GOST-R and SGS approvals, our wide range of products includes buttweld fittings, reducers, and flanges that are ready to be exported and meet quality standards for markets around the world. Manufacturers who are ISO 9001:2015 certified consistently offer quality and innovation in all industrial flanges applications, supporting essential flow systems in both home and business settings. Ready to elevate your next project with dependable industrial flanges? Contact our expert team at info@hb-steel.com to discuss your specific requirements and discover why leading companies worldwide trust RAYOUNG for their critical piping solutions.
References
1. American Society of Mechanical Engineers. "ASME B16.5 Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings: NPS 1/2 through NPS 24 Metric/Inch Standard." ASME International, 2020.
2. European Committee for Standardization. "EN 1092-1 Flanges and their joints - Circular flanges for pipes, valves, fittings and accessories, PN designated - Part 1: Steel flanges." CEN, 2018.
3. Japanese Industrial Standards Committee. "JIS B2220 Steel Pipe Flanges." Japanese Standards Association, 2019.
4. Bickford, John H. "An Introduction to the Design and Behavior of Bolted Joints." Fourth Edition, CRC Press, 2017.
5. Singh, Krishna P. "Mechanical Design of Heat Exchangers and Pressure Vessel Components." Arcturus Publishers, 2019.
6. Mohitpour, Moness. "Pipeline Design & Construction: A Practical Approach." Third Edition, ASME Press, 2018.

Need a quote? Want to see samples? Just say hello. We’re friendly. We’re fast. And we’re ready when you are.

Welcome to RAYOUNG – Strong Pipes, Stronger Promise




