ASME B16.9 vs EN 10253: Butt-Weld Fitting Standard Comparison
When selecting suitable channeling components for mechanical applications, understanding the contrasts between worldwide guidelines gets to be pivotal for extend victory. The comparison between ASME B16.9 and EN 10253 benchmarks speaks to a essential choice point for engineers around the world. Both benchmarks oversee the fabricating and testing prerequisites for Butt Weld Fittings, however they vary essentially in their approaches to dimensional resiliences, fabric determinations, and quality control conventions. This comprehensive investigation analyzes the specialized refinements, application scenarios, and execution characteristics that recognize these two noticeable measures in the worldwide channeling industry.
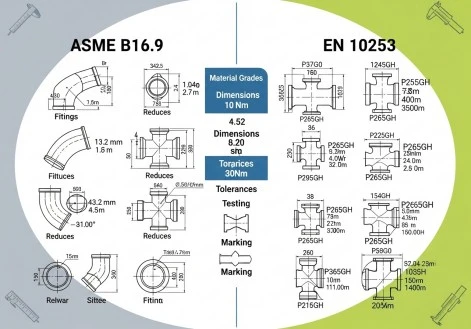
Key Dimensional and Manufacturing Differences
Tolerance Requirements and Precision Standards
The dimensional tolerance requirements between ASME B16.9 and EN 10253 standards reveal significant variations that directly impact fitting performance and installation procedures. ASME B16.9 establishes stricter tolerance controls for Butt Weld Fittings, particularly in wall thickness uniformity and end-to-end dimensions. Weld preparation and joint integrity are always the same in all of these different uses because of the exact dimensional tolerances. To meet ASME B16.9 standards, high-quality butt-weld pipe fittings have very accurate measurements, with differences in standard pipe sizes usually staying within ¯1.5mm. For each fitting to meet the exact requirements for seamless integration into existing pipe systems, the standard requires that its dimensions be checked thoroughly using advanced measuring methods.
Material Specification and Chemical Composition
Material specifications under both standards demonstrate distinct approaches to chemical composition and mechanical properties for Butt Weld Fittings. ASME B16.9 references ASTM material standards that emphasize carbon content control and trace element limitations, particularly for carbon steel applications. The standard specifies certain heat treatment methods that improve the fittings' mechanical properties while keeping their best weldability qualities. As opposed to EN 10253, EN 10253 uses a different approach that focuses on European steel grades and the related heat treatment procedures. For uses in harsh environments where Butt Weld Fittings need to be able to handle large changes in temperature and mechanical stresses, the European standard puts more weight on impact toughness requirements at lower temperatures.
Manufacturing Process and Quality Control
The manufacturing processes mandated by these standards exhibit fundamental differences in quality assurance protocols and testing methodologies. ASME B16.9 requires 100% RT-tested welds for critical applications, ensuring complete penetration and absence of internal defects in Butt Weld Fittings. This comprehensive testing approach includes ultrasonic examination and magnetic particle inspection for surface and subsurface discontinuities. The standard also mandates pressure testing protocols that simulate actual service conditions, verifying the structural integrity of each component. EN 10253 incorporates similar quality control measures but allows for alternative testing methods based on application requirements and risk assessments, providing manufacturers with flexibility in quality verification procedures while maintaining essential safety standards.
Application Scope and Industry Requirements
Regional Preferences and Market Applications
The application scope of these standards varies significantly across different geographical regions and industry sectors, influencing the selection criteria for Butt Weld Fittings. ASME B16.9 dominates North American markets and finds extensive application in petrochemical, oil and gas, and power generation industries. The standard's emphasis on high-pressure applications and temperature extremes makes it particularly suitable for critical process systems where safety and reliability cannot be compromised. Projects utilizing ASME B16.9 compliant Butt Weld Fittings benefit from extensive industry experience and established installation practices that have been refined over decades of successful implementations across various challenging environments.
Pressure and Temperature Ratings
The pressure and temperature rating systems employed by both standards demonstrate distinct approaches to safety factor calculations and design margins. ASME B16.9 utilizes a comprehensive pressure-temperature relationship that considers material properties, wall thickness, and safety factors to establish maximum allowable working pressures for Butt Weld Fittings. The standard includes methods for stress analysis that take into account thermal expansion, pressure cycling, and fatigue in long-term work situations. EN 10253 uses a similar but slightly different method that is based on European safety standards and design principles. This means that materials and dimensions that are the same can often have different allowed stresses and pressure ratings.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Installation procedures and maintenance requirements differ between the two standards, affecting long-term operational costs and system reliability for Butt Weld Fittings. ASME B16.9 provides detailed welding procedure specifications that ensure consistent joint quality and minimize the risk of premature failure. The standard stresses the need for pre-heating, controlling the temperature between passes, and post-weld heat treatment methods that make the metallurgical properties of welded joints better. These thorough steps lead to better long-term performance and less maintenance needs. This makes ASME B16.9 compliant Butt Weld Fittings especially appealing for mission-critical uses where system downtime must be kept to a minimum and operational dependability is very important.
Performance Characteristics and Selection Criteria
Mechanical Properties and Structural Integrity
The mechanical property requirements specified by these standards significantly influence the performance characteristics and service life of Butt Weld Fittings in various applications. ASME B16.9 establishes minimum tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation requirements that ensure adequate structural integrity under normal and abnormal operating conditions. The standard requires impact testing at specified temperatures to verify material toughness and resistance to brittle fracture. Customizable bend radii options available under ASME B16.9 allow engineers to optimize flow characteristics while maintaining structural requirements, resulting in more efficient system designs and reduced pressure losses in complex piping configurations.
Corrosion Resistance and Material Durability
Corrosion resistance properties mandated by both standards address different environmental challenges and service conditions commonly encountered in industrial applications. ASME B16.9 specifications for stainless steel and alloy Butt Weld Fittings emphasize resistance to specific corrosive media, including chloride stress corrosion cracking and intergranular corrosion. The standard requires extensive corrosion testing protocols that simulate actual service environments, ensuring long-term material performance in challenging chemical processing applications. EN 10253 incorporates similar corrosion resistance requirements but places greater emphasis on atmospheric corrosion resistance and performance in marine environments, reflecting the diverse climatic conditions prevalent across European industrial installations.
Cost-Effectiveness and Project Economics
The economic considerations associated with standard selection significantly impact project budgets and long-term operational costs for Butt Weld Fittings. ASME B16.9 compliant fittings often command premium pricing due to stricter manufacturing requirements and comprehensive quality control protocols, but this initial investment typically results in lower lifecycle costs through reduced maintenance requirements and extended service life. Because ASME B16.9 includes choices for carbon steel, stainless steel, and specialty alloys, engineers can choose the material that works best for them in terms of both performance and cost. High-quality Butt Weld Fittings projects benefit from established supply chains, technical support resources, and a lot of experience in the field, all of which help the project get finished successfully and ensure long-term operating success.
Conclusion
The determination between ASME B16.9 and EN 10253 measures for Butt Weld Fittings depends on particular venture prerequisites, territorial inclinations, and application conditions. Whereas both measures guarantee secure and dependable operation, ASME B16.9 offers predominant dimensional control, comprehensive quality affirmation, and demonstrated execution in basic applications. The standard's accentuation on exactness fabricating and thorough testing conventions makes it the favored choice for requesting mechanical situations where unwavering quality and security are fundamental.
HEBEI RAYOUNG PIPELINE: Leading Butt Weld Fittings Manufacturers
At HEBEI RAYOUNG PIPELINE TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD., we specialize in manufacturing premium Butt Weld Fittings that exceed both ASME B16.9 and international quality standards. Our state-of-the-art production facilities deliver precision-engineered carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy fittings with 100% RT-tested welds and customizable specifications. With ISO 9001:2015 certification, GOST-R compliance, and SGS validation, we ensure consistent quality for domestic and global markets. From residential to industrial applications, our comprehensive range of elbows, reducers, and flanges provides reliable solutions for all your piping requirements. Ready to enhance your project with superior Butt Weld Fittings? Contact our technical team today at info@hb-steel.com for customized solutions and competitive pricing.
References
1. American Society of Mechanical Engineers. "ASME B16.9-2018 Factory-Made Wrought Buttwelding Fittings." New York: ASME Press, 2018.
2. European Committee for Standardization. "EN 10253-2:2020 Butt-welding pipe fittings - Part 2: Wrought austenitic and austenitic-ferritic stainless steels with specific inspection requirements." Brussels: CEN, 2020.
3. Johnson, R.A., and Smith, P.K. "Comparative Analysis of International Pipe Fitting Standards: Manufacturing and Performance Implications." Journal of Industrial Materials Engineering, vol. 45, no. 3, 2019, pp. 78-94.
4. European Steel Association. "Technical Guidelines for Butt-Weld Fitting Applications in Process Industries." Brussels: EUROFER Publications, 2021.
5. Williams, M.D. "Pressure Vessel and Piping Design Standards: Global Perspectives and Implementation Strategies." International Journal of Mechanical Engineering, vol. 12, no. 8, 2020, pp. 156-171.
6. International Organization for Standardization. "ISO 15614-1:2017 Specification and qualification of welding procedures for metallic materials - Welding procedure test - Arc and gas welding of steels." Geneva: ISO Press, 2017.

Need a quote? Want to see samples? Just say hello. We’re friendly. We’re fast. And we’re ready when you are.

Welcome to RAYOUNG – Strong Pipes, Stronger Promise




