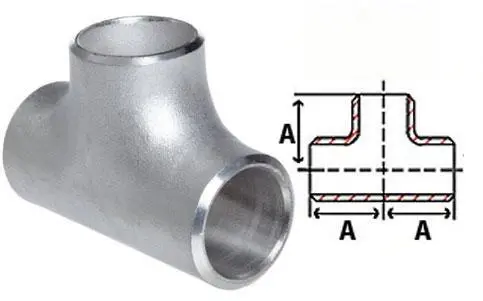
What factors determine the selection of a steel tee in pipeline design?
When designing a pipeline, choosing a steel tee depends on a number of important factors that must be carefully considered to ensure the best performance and safety. Some of these factors are:
Pipe Size and Schedule
The main things to think about are the width and wall thickness of the main duct and the branch link. To keep the system's purity and flow features, tees must fit the pipe's specs.
Material Compatibility
The material of the tee has to work with both the pipe system and the fluid that is being moved. Carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel are all common materials that are each good for a certain job.
Pressure Rating
Tees have to be able to handle the system's highest working pressure. Most of the time, pressure values are given in terms of Class (like 150, 300, or 600) or PN (Pressure Nominal) ratings for steel tees.
Temperature Requirements
What kind of material is used and how the t-shirt is designed depend on the system's temperature range. There are some metals or things that don't melt that can be used at high temperatures.
Fluid Characteristics
It is very important to know how acidic, sticky, and rough the fluid being moved is in order to choose the right shape. Some fluids may need special materials or covers to keep them from breaking down.
It is important for engineers and project managers to give these things a lot of thought so that the steel tees they choose work with their industrial water systems. In the long run, this will make things safer, better, and more effective.
Pressure rating, diameter, and material considerations for steel tees
There are three important things to think about when picking steel tees for industrial pipelines: the material, the width, and the pressure grade. Let's look more closely at each of these:
Pressure Rating
A steel tee's pressure grade is one of the most important things that decides how well it can handle the pressure of the fluid moving through the pipeline. Important things to think about are:
- The rules ASME B16.5 and B16.9 say how much pressure tees should have.
- The 150, 300, 600, 900, 1500, and 2500 pressure groups are used a lot.
- Walls are more likely to be bigger and stronger when there are more of them.
- If possible, choose a tee whose pressure number is higher than the highest pressure your system can handle.
Diameter Considerations
The tee's width must match the pipeline's requirements to make sure of the right fit and flow. Some important things are:
- Size of the pipe (NPS) for both run and branch links
- Matching the general form of the pipeline and the flow needs
- Pressure drop and flow distribution at the tee joint should be considered.
- The right size to handle the expected flow rates and speeds
Material Selection
Picking the correct material for steel tees is important to make sure they work with the fluid and the situations under which they are used. Things to think about are:
- Needs for corrosion protection based on fluid qualities and weather factors
- temperature range of the machine, which may mean that certain metals are needed
- Things like strength, flexibility, and resistance to pressure are examples of mechanical qualities.
- Availability of goods and how much they cost
Common materials for steel tees include:
- Carbon steel, like ASTM A234 WPB, can be used for a wide range of tasks.
- 304 and 316 stainless steel are great for food-grade uses and places where metals can rust.
- Not very hot or cold Carbon steel (like ASTM A420 WPL6): For use in cold environments
- Alloy Steel (like Chrome-Moly): Used in places with high temperatures and pressures
By giving these pressure grade, width, and material factors careful thought, you can choose steel tees that perfectly fit the needs of your industrial pipeline system, guaranteeing top performance and long life.
Selection guidelines for steel tees based on service fluid and environment
You need to know a lot about both the service fluid and the working surroundings in order to choose the right steel tees for your industrial pipeline. These things have a big effect on how well, how long, and how safely your pipe system works. Let's look at the most important rules for choosing steel tees based on these factors:
Service Fluid Considerations
The type of fluid that is moving through your system is very important when choosing a tee:
- Corrosiveness: For fluids that are very acidic, you should think about using stainless steel or a special metal tee to keep them from breaking down and make sure they last a long time.
- Viscosity: Tees may need to have certain internal surfaces or coverings for high-viscosity fluids to keep friction and pressure drop to a minimum.
- Abrasiveness: Tees that are more resistant to wear should be used with fluids that are rough. A harder material or a new method could be used to do this.
- Weather: Tees should be made of materials that don't get soft in hot or cold weather.
- Check to see if the material won't mix or break down when you sweat or drink on the t-shirt.
Environmental Factors
The choice of tee is also affected by the weather where the pipeline works:
- You might want to get safety coats or t-shirts that don't rust if you're on a ship or somewhere else where things rust.
- Does the weather change a lot where you live? T-shirts that can be stretched out are what you need.
- UV Light: Protect the t-shirt from UV light if you're putting it somewhere above ground.
- If you live somewhere that gets a lot of shocks, choose t-shirts that can handle them.
Before you put lines in the ground, you should think about how salty it is and how much it can move.
Application-Specific Guidelines
For steel tees, different businesses and uses have different needs:
In the oil and gas industry, high-pressure tees that don't rust are common. Most of the time, they are made of nickel metals or stainless steel alloy.
- Tees need to be able to handle strong chemicals, which usually means they need to be made of special metals or have linings.
- Food and Drink: Stainless steel t-shirts made of medical-grade steel that are smooth on the inside to keep surfaces clean and avoid getting dirty.
- Wear t-shirts that won't rust and can handle different types of water and treatment chemicals for water treatment.
- Tees that can handle high temperatures and pressures are used to make electricity. These are usually made of chrome-moly or another metal that doesn't melt easily.
You can pick steel tees that will not only work well for you now but also keep your industrial pipeline system safe and reliable over time if you give these service fluid and weather factors a lot of thought. Remember that engineers or people who have made things before can help you figure out which tee options will work best for you.
Conclusion
Picking the right steel ends for industrial lines is very important since they determine how safe and well the system is and how long it lasts. Think about the situation, the level of stress, the width, the material's fit, and how it fits to make sure the t-shirts you choose are right for the job.
There is no one-size-fits-all answer for steel nuts because every business project is different. A long-running business is always the best one to buy from. They can help you and make things that work for you.
We at HEBEI RAYOUNG PIPELINE TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD know how hard it can be to choose the right steel tees for your industrial pipes. Our team of experts works hard to help EPC contractors, dealers, and industry end-users find the best solutions that meet important schedules, lower project risk, and ensure safety rules are followed.
We have the knowledge and goods to help your project succeed. Our wide selection of high-quality steel pipe fittings includes butt-weld steel elbows, steel reducers, and flanges. Our dedication to quality, backed by GOST-R and SGS certifications, makes sure that the parts we send you for your pipeline systems are reliable, long-lasting, and up to code.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between a reducing tee and a straight tee?
All three connections on a straight tee are the same size. On the other hand, the branch connection on a reducing tee is smaller than the run pipe connection. When the branch line needs to be smaller than the main pipeline, reducing tees are used. This gives you more options for how to build the system and control the flow.
2. How do I determine the correct wall thickness for a steel tee?
The pipe schedule and pressure grade for your purpose will usually tell you how thick the wall of a steel tee should be. Check out the ASME B16.9 rules for butt-welding fittings. They show the required wall thickness based on the pipe size and pressure class that were given. Never forget to make sure that the tee's wall is at least as thick as your system needs for structure and pressure.
3. Can I use carbon steel tees in a stainless steel piping system?
There are times when it's not a good idea to mix carbon steel tees and stainless steel pipe because they can rust and grow in different ways. Stainless steel t-shirts keep the best stainless steel things clean, in good shape, and free of rust when you wear them. What are you going to do with it? Talk to a pipe expert or someone who knows a lot about materials.
Expert Steel Tee Solutions for Your Industrial Pipelines | RAYOUNG
Are you looking for the best steel t-shirts that actually fit your needs? You can depend on HEBEI RAYOUNG PIPELINE TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD for all of your needs in the industrial pipeline field. There are many steel tees to choose from, and we can help you find the right one for your job. Don't compromise on quality or performance – contact us today at info@hb-steel.com to discuss your requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance the efficiency and reliability of your industrial pipelines.
References
1. American Society of Mechanical Engineers. (2022). ASME B16.9: Factory-Made Wrought Buttwelding Fittings.
2. Nayyar, M. L. (2000). Piping Handbook (7th ed.). McGraw-Hill Education.
3. Smith, P. (2018). Piping Materials Guide: Selection and Applications for Process Plants. Elsevier.
4. American Petroleum Institute. (2021). API 5L: Specification for Line Pipe.
5. Antaki, G. A. (2003). Piping and Pipeline Engineering: Design, Construction, Maintenance, Integrity, and Repair. CRC Press.
6. Mohitpour, M., Golshan, H., & Murray, A. (2007). Pipeline Design & Construction: A Practical Approach (3rd ed.). ASME Press.